In today’s digital age, organizations accumulate a significant number of IT assets, including computers, servers, smartphones, and other electronic devices. As these assets reach the end of their lifecycle, it becomes crucial to manage their disposition responsibly; Recycle Reuse eWaste.
IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) is a critical component of an organization’s IT lifecycle management. By implementing secure, compliant, and environmentally-friendly ITAD practices, organizations can protect sensitive data, comply with regulations, and contribute to sustainability efforts. As the volume of electronic devices continues to grow, adopting best practices in ITAD becomes increasingly important for both operational efficiency and corporate responsibility.
ITAD (IT Asset Disposition) refers to the process of securely disposing of obsolete or unwanted IT equipment in a manner that ensures data security and environmental responsibility. For more details, visit ITAD Overview by TechTarget.IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) involves the strategic management and recycling of outdated or surplus IT assets, with a focus on data protection and compliance. To learn more, check out Blancco’s ITAD Solutions. The practice of ITAD ensures that retired IT hardware is properly handled to prevent data breaches and environmental harm. For additional information, see Arrow Electronics’ ITAD Services.
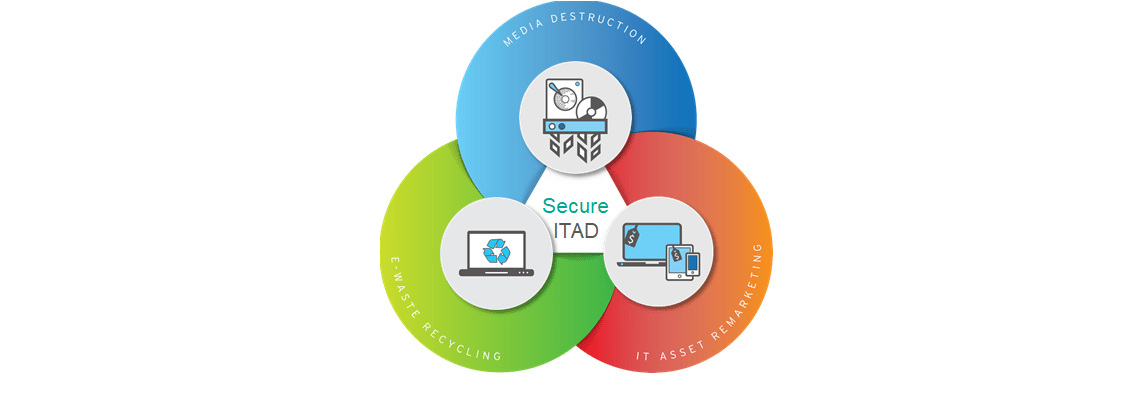
IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) refers to the process of securely and environmentally-friendly disposing of or repurposing these electronic assets. Proper ITAD practices ensure data security, regulatory compliance, and environmental sustainability.
ITAD Process
1. Assessment and Planning
The first step in the ITAD process is assessing the inventory of IT assets due for disposition. Organizations should catalog these assets, noting their condition, age, and any sensitive data they may contain. Based on this assessment, a comprehensive ITAD plan is developed, outlining the methods for data destruction, recycling, and remarketing.
2. Data Destruction
Data destruction is a critical phase in ITAD to ensure that no sensitive information remains on disposed assets. Common methods include:
- Data Wiping: Overwriting the data on storage devices to prevent data recovery.
- Degaussing: Using strong magnetic fields to erase data from magnetic storage devices.
- Physical Destruction: Shredding or crushing storage devices to ensure data cannot be retrieved.
3. Recycling and Disposal
After data destruction, IT assets are either recycled or disposed of following environmental guidelines. Recyclable materials are extracted, and hazardous components are handled according to regulatory standards. Certified e-waste recyclers ensure that electronic waste is processed responsibly.
4. Remarketing and Resale
Some IT assets, particularly those in good condition, can be refurbished and resold. Remarketing extends the lifecycle of electronic devices, providing economic benefits and reducing waste. Organizations can recover some of their initial investment by selling refurbished assets in secondary markets.
5. Documentation and Reporting
Proper documentation is essential throughout the ITAD process. Detailed records of data destruction, recycling, and resale activities provide an audit trail for compliance purposes. Organizations should maintain certificates of data destruction and recycling to demonstrate adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Benefits of ITAD – Recycle Reuse eWaste
Enhanced Data Security
Implementing robust ITAD practices significantly reduces the risk of data breaches. Secure data destruction methods ensure that sensitive information is irretrievable, protecting organizations from potential security threats.
Compliance Assurance
By following ITAD best practices, organizations can ensure compliance with various data protection regulations. This not only helps avoid legal penalties but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
Environmental Sustainability
Responsible ITAD practices contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing e-waste and promoting recycling. This aligns with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals and enhances the organization’s reputation as an environmentally-conscious entity.
Cost Savings and Recovery
Effective ITAD strategies can lead to cost savings through the resale of refurbished assets. Organizations can recover a portion of their investment in IT equipment, making the disposition process economically beneficial.